This tutorial marks the beginning of a series of network security and penetration testing articles that I will be posting on this website.
Mar 26, 2013 Nmap for Mac OS X Explores Networks, Scans Ports, and More Mar 26, 2013 - 9 Comments Nmap is a powerful command line network discovery utility that lets you review network inventory, host response and uptime, and perform security auditing through port scans, OS and firewall detection, and more. Nmap Package Description. Nmap (“Network Mapper”) is a free and open source (license) utility for network discovery and security auditing. Many systems and network administrators also find it useful for tasks such as network inventory, managing service upgrade schedules, and monitoring host or service uptime. Nov 19, 2019 This package contains Nmap, Zenmap, Ncat, Ndiff, and Nping. It is intended to work on Intel and PowerPC Macs running Mac OS X 10.4.11 or later. Installation of all packages is optional. Unselect Zenmap to get just the command-line tool. Unselect Nmap if you prefer to use a copy of Nmap that is already installed. Zenmap will not work without Nmap.
The purpose of this article is to describe how to perform a simple NMAP scan of an IP range/subnet on a network. There are hundreds of scan options with NMAP but I will start with the most useful one which is to scan a range of IP addresses together with some other extra options.
NOTE: For a more comprehensive NMAP Tutorial with all popular and useful commands you can download this Nmap Cheat Sheet PDF here.
One of my responsibilities in the company I work is to perform security assessments and penetration testing on the external and internal systems of the enterprise. The tool that I use in almost all penetration testing engagements is the famous NMAP scanner (short for Network Mapper tool).
In a penetration testing project you need first to “map” and identify as much information about your targets so that to plan your next steps. This is the reconnaissance phase of a security test.
NMAP is an excellent utility to help you in the reconnaissance phase since you can collect information such as:
- What IP addresses are live on the network (i.e what IPs have hosts running on them).
- What ports are open on these IP addresses.
- What services are running on the open ports (together with service versions etc).
- What operating systems are running on the identified IP addresses.
- Find well known vulnerabilities on the scanned systems (using NSE scripts).
- Verify firewall rules.
- And much more
Now let’s go ahead and see several nmap options to scan multiple IP addresses in a network.
Simple NMAP scan of IP range
The default scan of nmap is to run the command and specify the IP address(es) without any other options. In this default scan, nmap will run a TCP SYN connection scan to 1000 of the most common ports as well as an icmp echo request to determine if a host is up.
There are four ways to scan multiple IP addresses:
Nmap For Mac High Sierra
1) Specify IPs one-by-one separated by space
nmap 192.168.10.1 192.168.10.111 192.168.10.222
Starting Nmap 7.12 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2016-04-25 21:55 GTB Daylight Time
Nmap scan report for 192.168.10.1
Host is up (0.0032s latency).
Not shown: 998 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
80/tcp open http
20031/tcp filtered unknown
MAC Address: D8:D4:3C:F2:AA:79 (Sony)
Nmap scan report for 192.168.10.111
Host is up (0.0056s latency).
Not shown: 991 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
21/tcp open ftp
22/tcp open ssh
80/tcp open http
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
443/tcp open https
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
873/tcp open rsync
3493/tcp open nut
8080/tcp open http-proxy
MAC Address: 00:08:9B:8B:F5:EB (ICP Electronics)
Nmap scan report for 192.168.10.222
Host is up (0.0022s latency).
Not shown: 996 filtered ports
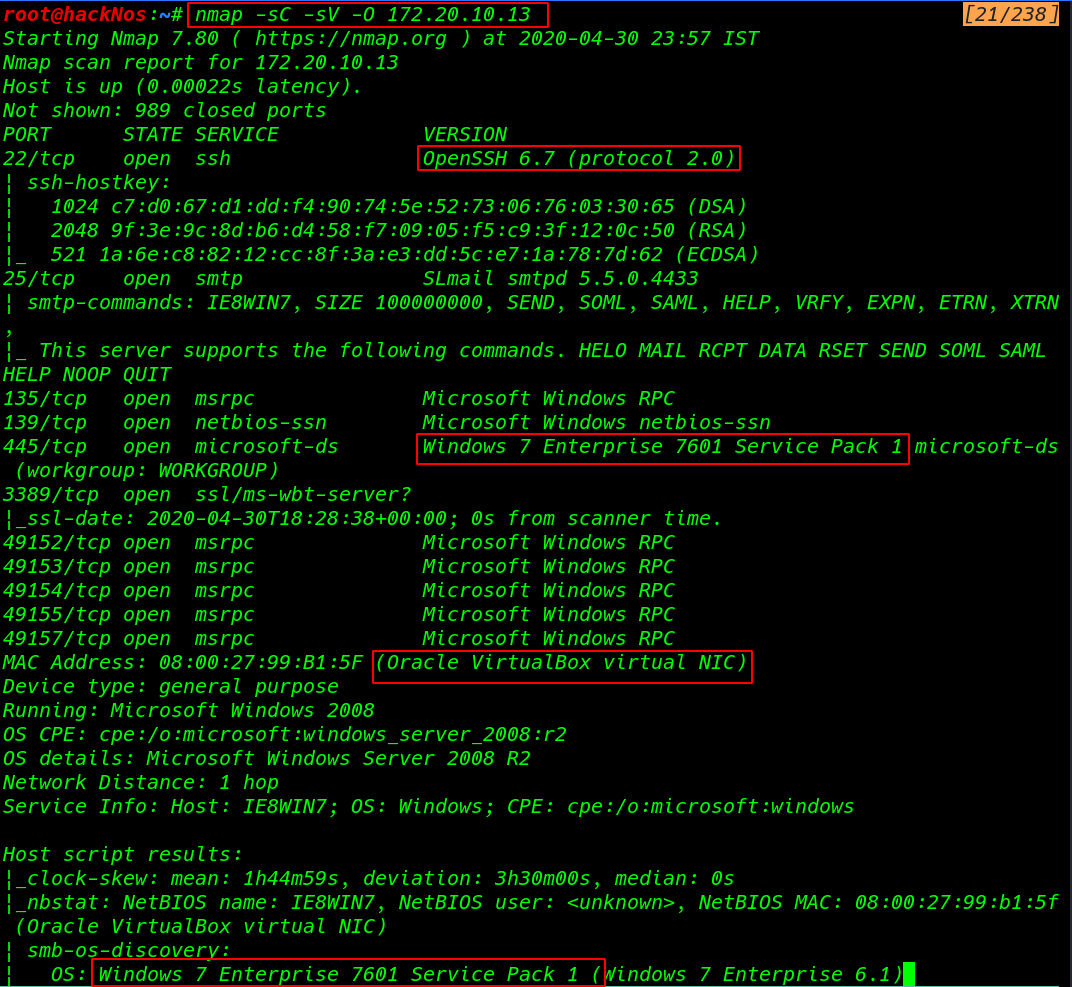
PORT STATE SERVICE
135/tcp open msrpc
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
5357/tcp open wsdapi
MAC Address: 00:1A:4D:58:1A:06 (Giga-byte Technology)
Nmap done: 3 IP addresses (3 hosts up) scanned in 11.46 seconds
2) Specify IPs in consecutive range
nmap 192.168.10.100-230 Tropico 4 for mac download.
Starting Nmap 7.12 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2016-04-25 22:03 GTB Daylight Time
Nmap scan report for 192.168.10.111
Host is up (0.0029s latency).
Not shown: 991 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
21/tcp open ftp
22/tcp open ssh
80/tcp open http
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
443/tcp open https
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
873/tcp open rsync
3493/tcp open nut
8080/tcp open http-proxy
MAC Address: 00:08:9B:8B:F5:EB (ICP Electronics)
Nmap scan report for 192.168.10.222
Host is up (0.0097s latency).
Not shown: 996 filtered ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
135/tcp open msrpc
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
5357/tcp open wsdapi
MAC Address: 00:1A:4D:58:1A:06 (Giga-byte Technology)
Nmap done: 131 IP addresses (2 hosts up) scanned in 6.52 seconds
3) Specify a scan range of IPs using a wildcard
nmap 192.168.10.*
4) Specify a scan range of IPs using a subnet notation
nmap 192.168.10.0/24
Scan all ports of an IP range
The simple default scan above will check the 1000 most well known ports for each IP address. What if you want to scan ALL ports of the IP range under scope. Let’s see how to run this:
Assume we want to find all open ports in class C subnet 192.168.10.0/24
1st way
nmap -p- 192.168.10.0/24
2nd way
nmap -p 1-65535 192.168.10.0/24
Discover Live IPs in a subnet
This is a “ping scan” to identify live hosts in the specified range.
This scan option uses a combination of scan techniques to identify live hosts, such as sending an icmp echo request, TCP SYN packets to ports 80 and 443, timestamp requests, arp requests etc.
nmap -sP 192.168.10.0/24
Detect OS and Services Running in a subnet
Now we will see how to scan a range of IPs and detect what Operating System and Services (versions) are running on live hosts.
nmap -A 192.168.10.0/24
Nmap For Macbook Air
There are hundreds of other nmap scan options available which will be covered in future posts, so stay tuned J
Related Posts
Nmap has supported Mac OS X since 2001, and our support has only improved over time. While Mac users can compile Nmap themselves, we also offer an executable installer. Nmap makes use of Jhbuild and gtk-mac-bundler which are used to build other projects for Mac OS X, such as OpenSSL, libapr, libsvn.. Nmap is also available through systems such as MacPorts and Fink which package Unix software for Mac OS X.
The easiest way to install Nmap and Zenmap on Mac OS X is to useour installer. TheMac OS X section ofthe Nmap download page provides a file namednmap-, where<version>.dmg<version> is the version number of the mostrecent release. The.dmgfile is known as a“disk image”. Installation instructions follow:
Download the file
nmap-.Double-click the icon to open it. (Depending on how you downloaded thefile, it may be opened automatically.)<version>.dmgThe contents of the disk image will be displayed. One ofthe files will be a Mac meta-package file named
nmap-.Open it to start the installer.<version>.mpkgOn OS X 10.8 and later, you may see a dialog likeFigure 2.2.
Figure 2.2. Apple Gatekeeper block screen
If this happens, it is necessary to right-click or control-click on the.mpkgand select “Open”,as shown inFigure 2.3.Figure 2.3. Apple Gatekeeper Open menu
A dialog similar to the first will appear, this time having an“Open” button (shown inFigure 2.4).Click the button to continue.Figure 2.4. Apple Gatekeeper Open screen
Follow the instructions in theinstaller. You will be asked for your password since Nmap installs in a system directory.
Once the installer is finished, eject the disk image bycontrol-clicking on its icon and selecting“Eject”. The disk image may now be placed inthe trash.
See the instructions in the section called “Executing Nmap on Mac OS X” forhelp on running Nmap and Zenmap after they are installed.
The programs installed by the installer will run on Intel Mac OS X 10.5(Leopard) or later. Users of earlier versions will have to compile fromsource or use a third-party package. Instructions for PowerPC (PPC) Mac systems (which Apple ceased selling in 2006) are available on our wiki.
Compiling Nmap from source on Mac OS X is no more difficult thanon other platforms once a proper build environment is in place.
Compiling Nmap on Mac OS X requiresXcode,Apple's developer tools that include GCC and the rest of the usual buildsystem. Xcode is not installed by default, but can be downloaded free ofcharge from the Mac AppStore. After installing Xcode, open“Preferences”, select the“Downloads” tab, and click the“Install” next to “Command LineTools”.

Xcode installations don't always include the command line tools. You can install them by opening Xcode from the Applications folder, opening Preferencechoosing the Download header icon and clicking the Install button next to “Command Line Tools”.
Once you have installed Xcode and the command-line tools, follow the compilation instructions found in the section called “Linux/Unix Compilation and Installation from Source Code”. Note that on some older versions of Mac OS X, you may have to replace the command ./configure with ./configure CPP=/usr/bin/cpp. Also, on some newer Mac OS X versions, the libpcap version of the library provided by Apple may be too old. You may have to configure Nmap with the command ./configure --with-libpcap=included in order to use the compatible version included in Nmap, or you should update the libpcap installed on your machine.
Zenmap depends on some external libraries that do not come withMac OS X, including GTK+ and PyGTK. These libraries have many dependenciesof their own. A convenient way to install all of them is to use athird-party packaging system as described inSection . Once the dependencies areinstalled, follow the instructions in the section called “Linux/Unix Compilation and Installation from Source Code” toinstall Zenmap as usual.
Another option for installing Nmap is to use a systemwhich packages Unix software for Mac OS X. The two discussed here areFink andMacPorts. See therespective projects' web sites for how to install the packagemanagers.
To install using Fink, run the command fink installnmap. Nmap will be installed as/sw/bin/nmap. To uninstall use the commandfink remove nmap.
To install using MacPorts, run sudo portinstall nmap. Nmap will be installed as/opt/local/bin/nmap. To uninstall, runsudo port uninstall nmap.
These systems install the nmapexecutable outside the global PATH. To enable Zenmap tofind it, set the nmap_command_path variable inzenmap.conf to /sw/bin/nmap or/opt/local/bin/nmap as described inthe section called “The nmap Executable”.
The terminal emulator in Mac OS X is calledTerminal, and is located in the directory/Applications/Utilities. Open it and aterminal window appears. This is where you will type your commands.
By default the root user is disabled on Mac OS X. To run a scan withroot privileges prefix the command name withsudo,asin sudo nmap -sS <target>.You will be asked for a password, which is just your normal loginpassword. Only users with administrator privileges can do this.
Zenmap requires the X11 application tobe installed. If it was not installed by default it may be available asan optional install on the Mac OS X installation discs.
When Zenmap is started, a dialog is displayed requesting that youtype your password. Users withadministrator privilegesmay enter theirpassword to allow Zenmap to run as the root user and run more advancedscans. To run Zenmap in unprivileged mode, select the“Cancel” button on this authentication dialog.
